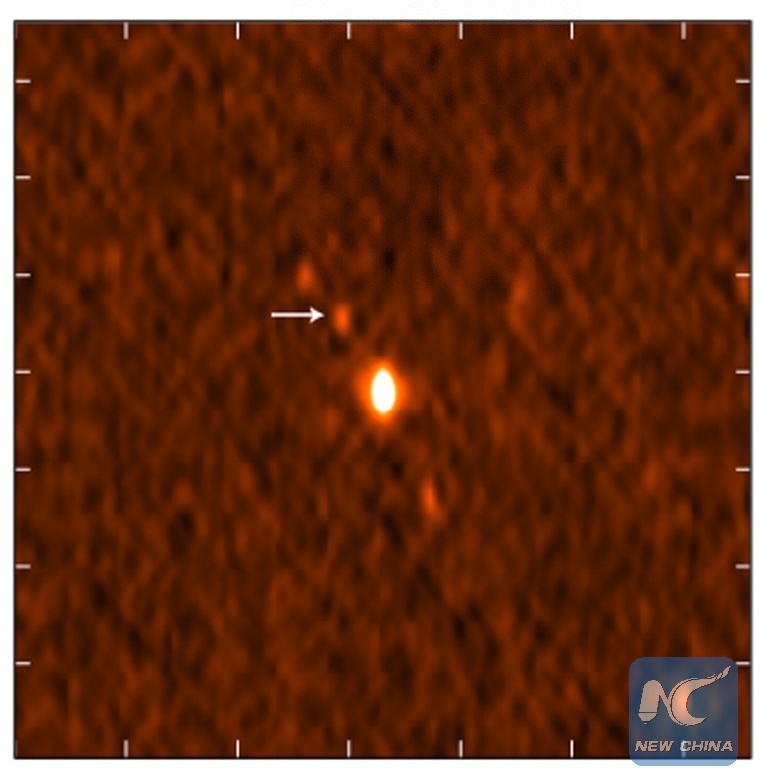

Radio image shows the GW170817 neutron star merger. Scientists announced Monday that they have for the first time detected the ripples in space and time known as gravitational waves as well as light from a spectacular collision of two neutron stars. (Xinhua/Gregg Hallinan of Caltech and Kunal Mooley of Oxford University)
WASHINGTON, Dec. 21 (Xinhua) -- The first observations of a neutron-star merger in both gravitational waves and light were named on Thursday by the influential U.S. journal Science as 2017's Breakthrough of the Year.
It's the second year in a row that editors of the U.S. scientific magazine have awarded its highest yearly honor to a discovery linked to gravitational waves, the ripples in space and time caused by the most powerful and energetic events in the universe.
"Gravitational waves are the gift that keeps on giving," explained Science News Editor Tim Appenzeller. "Being able to get the full picture of violent events like this promises to transform astrophysics, and that made this year's observation the clear Breakthrough for 2017."
Originally predicted in the early 20th century by Albert Einstein, gravitational waves were not detected until 2015, when the U.S. Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) identified a signal caused by two black holes spiraling towards each other and merging.
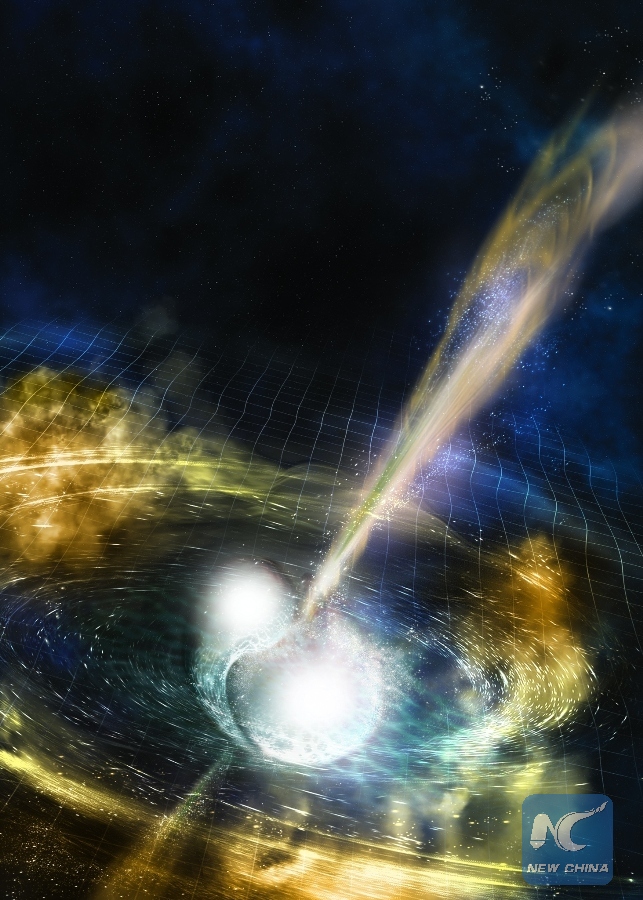

Illustration Image shows two merging neutron stars. The narrow beams represent the gamma-ray burst while the rippling spacetime grid indicates the isotropicgravitational waves that characterize the merger. Swirling clouds of material ejected from the merging stars are a possible source of the light that was seen at lower energies. Scientists announced Monday that they have for the first time detected the ripples in space and time known as gravitational waves as well as light from a spectacular collision of two neutron stars. (Xinhua/National Science Foundation/LIGO/Sonoma State University/A. Simonnet.)
It's a major discovery that won the Nobel Prize in Physics this year, in addition to landing Science's Breakthrough of the Year for 2016.
Then, on Aug. 17 this year, scientists not only, for the first time, observed the space tremor from a collision of two neutron stars 130 million light years away using the LIGO detectors, they also saw the event at all wavelengths of light, from gamma rays all the way to radio, with ground- and space-based telescopes.
"The explosion was easily the most-studied event in the history of astronomy: Some 3,674 researchers from 953 institutions collaborated on a single paper summarizing the merger and its aftermath," Science staff writer Adrian Cho wrote in an accompanying article.
Cho highlighted the importance of using gravitational waves as a new way of observing the universe.
"The blast confirmed several key astrophysical models, revealed a birthplace of many heavy elements, and tested the general theory of relativity as never before," he said.
Cho further noted that the merger only "whetted astrophysicists' appetites for more data."
"Researchers plan to increase LIGO's sensitivity at high frequencies -- for instance, by manipulating the laser light circulating in the massive detectors -- but doing so may take a few years," he added.
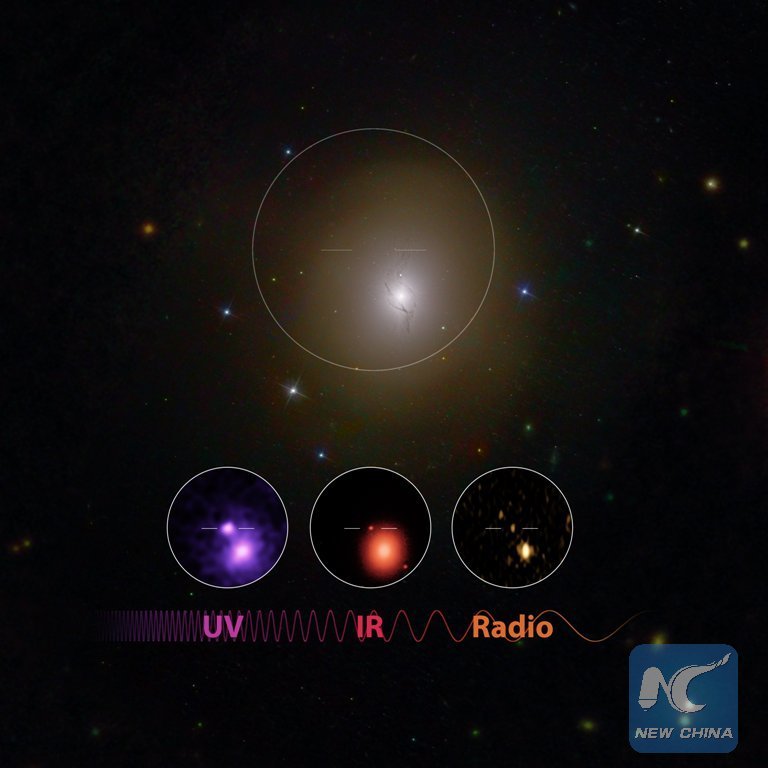
Image made by Caltech and NASA shows the UV/IR/Radio discovery of neutron star merger in NGC 4993. Scientists announced Monday that they have for the first time detected the ripples in space and time known asgravitational waves as well as light from a spectacular collision of two neutron stars.
(Xinhua/Robert Hurt of Caltech, Mansi Kasliwal of Caltech, Gregg Hallinan of Caltech, Phil Evans of NASA and the GROWTH collaboration)
Jeremy Berg, the editor-in-chief of Science, said in an accompany editorial that the multidimensional, detailed observations of the collision of two neutron stars represent "an exciting new phase of astronomy with tremendous potential for the future -- and a great example of 'big science.'"
"Although discoveries from LIGO have been relatively rapid, they overlie a long history of painstaking work by scientists and engineers, as well as patient support from the U.S. National Science Foundation, which has invested 1.1 billion U.S. dollars in LIGO since 1990," he wrote.
"For those directly involved, it must be extraordinarily gratifying to see decades of effort come to fruition in such a spectacular fashion and to have made such contributions to truly universal questions."
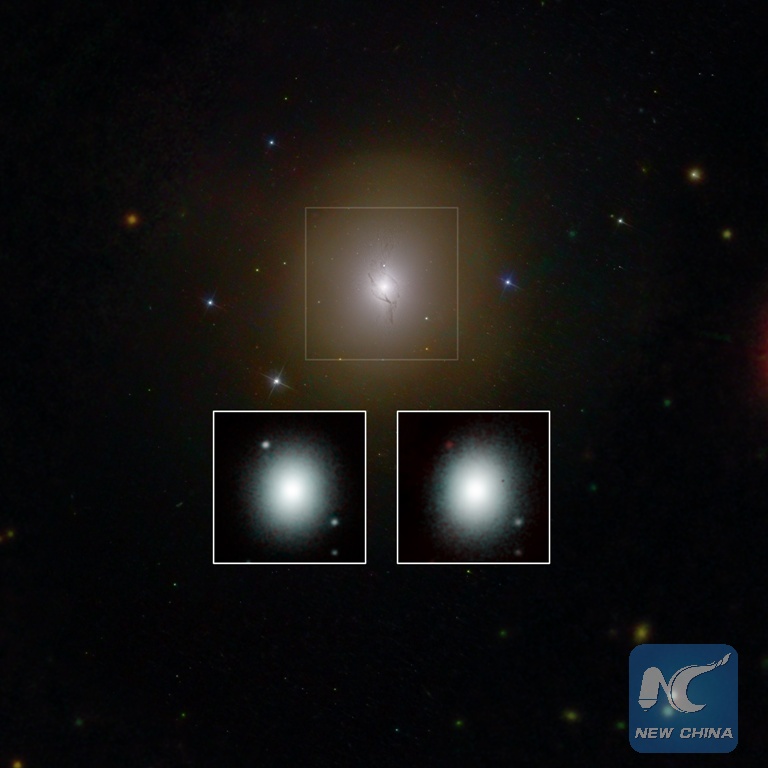
Image made by Caltech and NASA shows the evolution of neutron star merger confirming heavy element synthesis. Scientists announced Monday that they have for the first time detected the ripples in space and time known asgravitational waves as well as light from a spectacular collision of two neutron stars.
(Xinhua/Robert Hurt of Caltech, Ryan Lau of Caltech, Leo Singer of NASA, Mansi Kasliwal of Caltech and the GROWTH collaboration)
Other scientific achievements in the journal's annual top 10 list included:
-- Scientists identified a new species of orangutan on the Indonesian island of Sumatra-the first great ape species to be discovered since the bonobo in 1926.
-- A technique called cryo-electron microscopy provided fresh insights this year into many of life's key molecules, and is fast reshaping the field of structural biology.
-- Following their colleagues in physics, biologists posted unreviewed papers known as preprints online in record numbers this year, leading to "a major cultural change in communication."
-- Biologists made a big advance in editing DNA and RNA, developing techniques to transform one nucleotide base into another at a precise point in a genome.
-- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first drug to treat solid tumors based not on where it originated, but on a particular genetic defect.
-- Scientists drilled and retrieved a 2.7-million-year-old ice core from Antarctica, which is 1.7 million years older than any previous ice sample.
-- Paleoanthropologists determined that a Homo sapiens skull from Morocco is 300,000 years old, pushing back our species origins by 100,000 years.
-- The U.S. FDA approved three gene therapy products, the first of their kind.
-- Physicists used a detector the size of a milk jug to observe neutrinos pinging off atomic nuclei in a way never seen before, confirming a 40-year-old prediction and opening the way for portable detectors of these elusive particles.

